KI:STE
AI Strategy for Earth system data
About KI:STE
The KISTE project aimed to exploit recent developments in artificial intelligence – especially deep learning methods – for sound environmental data analysis. The scientific goal was the implementation of current AI approaches for spatiotemporal variable pattern recognition and pattern analysis in environmental data in the subject areas clouds, geohazards, water, air quality and vegetation within the framework of five dissertations. During this time, a technical platform was created to make powerful AI applications on environmental data portably available. An online AI learning platform with various interfaces for this AI platform was set up for this purpose. This e-learning offer is aimed at the location-independent education of young scientists and other interested parties. It will use the concepts and methods developed in the five research fields as teaching material.

Work packages
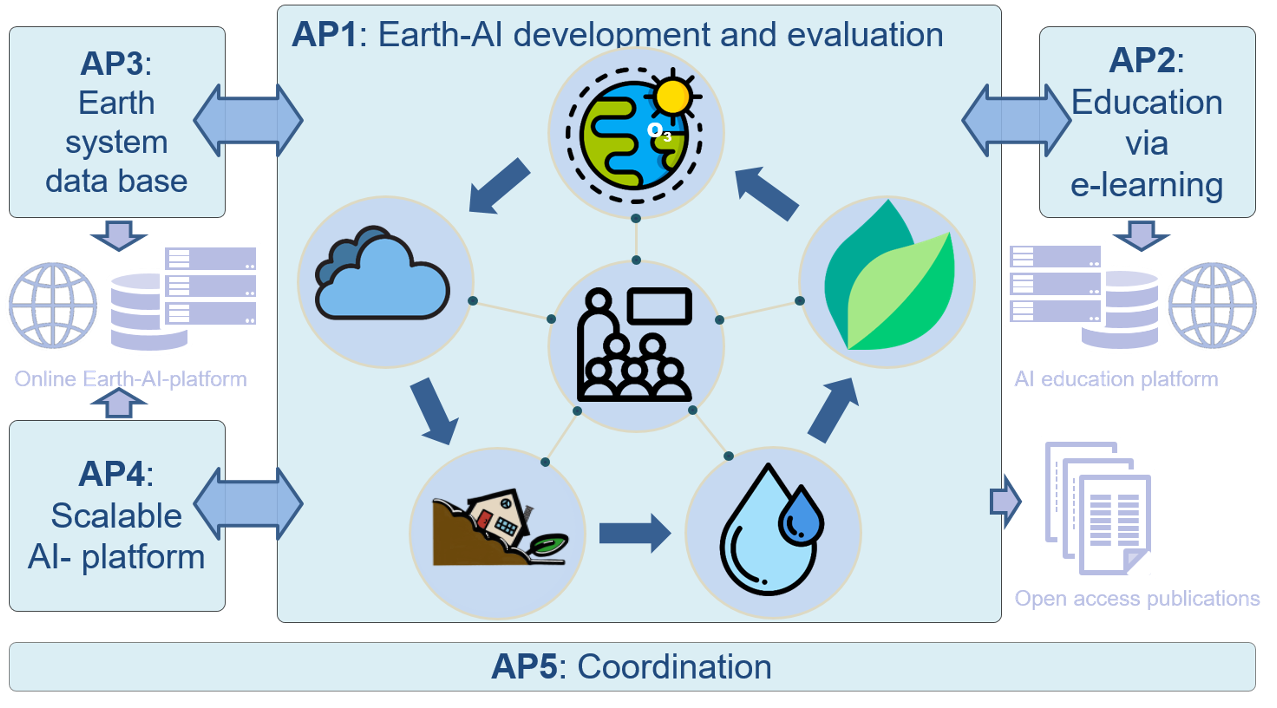
Clouds
Improved predictability of the availability of solar energy through the analysis of spatial-temporal patterns of cloud parameters based on geostationary satellite observations
Geohazards
Development of a generic and FAIR susceptibility and hazard mapping framework for facilitated and streamlined geohazard mapping , as well as analysis of sensitivity of ml-based mapping on various research study-specific design parameters to support transparency and reliability.
Water
Improve predictions of droughts or floods by examining extreme hydrometeorological events from the combination of simulation and observation data
Air quality
Air quality: Development of a methodology for seasonal forecasts of extreme values of air pollution by examining the influence of plant health on air quality
Vegetation
Development of multi-task methods to predict several parameters of the plant condition simultaneously, especially with regard to extreme events.
AI lighthouse for the environment, climate, nature and resources
KISTE is part of the initiative “AI light house for the environment, climate, nature and resources”. These are projects that use their digital know-how and creativity to overcome ecological challenges.
Project Partners

HDS-LEE

Latest News

Using atmospheric understanding to exploit multi-spectral images
Ankit Patnala published his first paper in the IEEE journal. There is yet more information currently unused by machine learning in satellite data. Natural images

Can Deep Learning close the Gap between terrestrial modeled Data and Observations?
Within the HDS-LEE graduate school, Kaveh P. Yousefi presented his U-Net capable of improving model-based precipitation and surface pressure fields towards observations.
Jungle-Net Poster presentation
Within the HDS-LEE graduate school and the ISPRS congress Timo Stomberg presented his Jungle-Net capable of giving insights into wilderness using explainable machine learning.

KI:STE Project Meeting
The KI:STE consortium meets on the 15th and 16th of November to exchange their latest scientific results, get insights to the newest functionalities of the

Lecture on Explainable Machine Learning for Earth Science
The live stream of Prof. Dr. Ribana Roscher’s lecture on explainable machine learning can be found here on YouTube. The lecture has two parts. The

KI:STE OpenGeoHub Summer School 2022
Following a long tradition of OpenGeoHub Summer Schools, the KI:STE project took the opportunity to co-host this year’s Summer School on Earth system data analysis.









